图形拟合(二):多边形拟合
算法
使用拉默-道格拉斯-普克演算法(Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm),对应的解析可以参考:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ramer%E2%80%93Douglas%E2%80%93Peucker_algorithm
在OpenCV中也有实现,对应 approxPolyDP 函数。用法可以参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/k1412/p/6884484.html
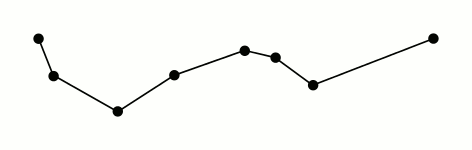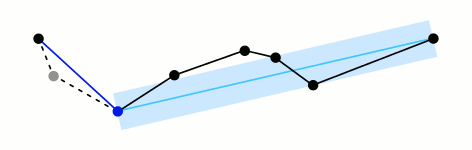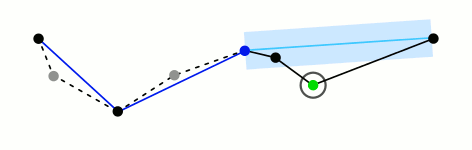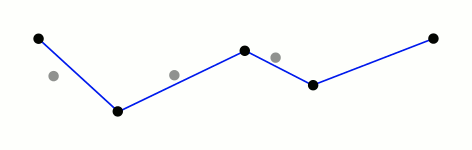
JavaScript版本实现
class Point {
x : number
y : number
constructor(_x : number, _y : number) {
this.x = _x
this.y = _y
}
}
class Range {
start : number
end : number
constructor(_start : number, _end : number) {
this.start = _start
this.end = _end
}
}
class MiniOpenCV {
static approxPolyDP_(
src_contour : Point[],
count0 : number,
dst_contour : (Point | any)[],
is_closed0 : boolean,
eps : number,
_stack : (Range | any)[]
): number {
let init_iters = 3;
let slice = new Range(0, 0);
let right_slice = new Range(0, 0);
let start_pt = new Point(-1000000, -1000000)
let end_pt = new Point(0, 0);
let pt = new Point(0, 0);
let i = 0, j, pos = 0, wpos, count = count0, new_count = 0;
let is_closed = is_closed0;
let le_eps = false;
let top = 0, stacksz = _stack.length;
let stack = _stack;
const PUSH_SLICE = (slice : Range) => {
if (top >= stacksz) {
stacksz = Math.ceil(stacksz * 3 / 2);
stack.length = stacksz;
}
stack[top++] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(slice))
}
const READ_PT = (pos : number): [Point, number] => {
const pt = src_contour[pos];
if ((++ pos) >= count) {
pos = 0;
}
return [pt, pos]
}
const READ_DST_PT = (pos : number): [Point, number] => {
const pt = dst_contour[pos]
if ((++ pos) >= count) {
pos = 0;
}
return [pt, pos]
}
const WRITE_PT = (pt : Point) => {
dst_contour[new_count++] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(pt));
}
if (count === 0) {
return 0;
}
eps *= eps;
if (!is_closed) {
right_slice.start = count;
end_pt = src_contour[0];
start_pt = src_contour[count - 1];
if (start_pt.x != end_pt.x || start_pt.y != end_pt.y) {
slice.start = 0;
slice.end = count - 1;
PUSH_SLICE(slice);
} else {
is_closed = true;
init_iters = 1;
}
}
if (is_closed) {
// 1. Find approximately two farthest points of the contour
right_slice.start = 0;
for (i = 0; i < init_iters; i++) {
let dist, max_dist = 0;
pos = (pos + right_slice.start) % count;
[start_pt, pos] = READ_PT(pos);
for (j = 1; j < count; j++) {
let dx, dy;
[pt, pos] = READ_PT(pos);
dx = pt.x - start_pt.x;
dy = pt.y - start_pt.y;
dist = dx * dx + dy * dy;
if (dist > max_dist) {
max_dist = dist;
right_slice.start = j;
}
}
le_eps = max_dist <= eps;
}
// 2. initialize the stack
if (!le_eps) {
right_slice.end = slice.start = pos % count;
slice.end = right_slice.start = (right_slice.start + slice.start) % count;
PUSH_SLICE(right_slice);
PUSH_SLICE(slice);
} else {
WRITE_PT(start_pt);
}
}
// 3. run recursive process
while (top > 0) {
slice = stack[--top];
end_pt = src_contour[slice.end];
pos = slice.start;
[start_pt, pos] = READ_PT(pos);
if (pos != slice.end) {
let dx, dy, dist, max_dist = 0;
dx = end_pt.x - start_pt.x;
dy = end_pt.y - start_pt.y;
while (pos != slice.end) {
[pt, pos] = READ_PT(pos);
dist = Math.abs((pt.y - start_pt.y) * dx - (pt.x - start_pt.x) * dy);
if (dist > max_dist) {
max_dist = dist;
right_slice.start = (pos + count-1) % count;
}
}
le_eps = max_dist * max_dist <= eps * (dx * dx + dy * dy);
} else {
le_eps = true;
// read starting point
start_pt = src_contour[slice.start];
}
if (le_eps) {
WRITE_PT(start_pt);
} else {
right_slice.end = slice.end;
slice.end = right_slice.start;
PUSH_SLICE(right_slice);
PUSH_SLICE(slice);
}
}
if (!is_closed) {
WRITE_PT(src_contour[count - 1]);
}
// last stage: do final clean-up of the approximated contour -
// remove extra points on the [almost] straight lines.
is_closed = is_closed0;
count = new_count;
pos = is_closed ? count - 1 : 0;
[start_pt, pos] = READ_DST_PT(pos);
wpos = pos;
[pt, pos] = READ_DST_PT(pos);
let t = Number(!is_closed);
for (i = t; i < count - t && new_count > 2; i++) {
let dx, dy, dist, successive_inner_product;
[end_pt, pos] = READ_DST_PT(pos);
dx = end_pt.x - start_pt.x;
dy = end_pt.y - start_pt.y;
dist = Math.abs((pt.x - start_pt.x) * dy - (pt.y - start_pt.y) * dx);
successive_inner_product = (pt.x - start_pt.x) * (end_pt.x - pt.x) +
(pt.y - start_pt.y) * (end_pt.y - pt.y);
if (dist * dist <= 0.5 * eps * (dx * dx + dy * dy) && dx != 0 && dy != 0 && successive_inner_product >= 0) {
new_count--;
dst_contour[wpos] = start_pt = end_pt;
if ((++wpos) >= count) {
wpos = 0;
}
[pt, pos] = READ_DST_PT(pos);
i++;
continue;
}
dst_contour[wpos] = start_pt = pt;
if (++wpos >= count) wpos = 0;
pt = end_pt;
}
if (!is_closed) {
dst_contour[wpos] = pt;
}
return new_count;
}
static approxPolyDP(_curve: Point[], epsilon: number, closed: boolean) {
if (epsilon < 0.0 || !(epsilon < 1e30)) {
console.error("Epsilon not valid.");
}
let npoints = _curve.length;
if (!npoints) {
return {
points: [],
count: 0
}
}
let _stack = new Array(npoints)
let _buf = new Array(npoints)
let nout = MiniOpenCV.approxPolyDP_(_curve, npoints, _buf, closed, epsilon, _stack);
return {
points: _buf.filter((p: Point) => !!p),
count: nout
};
}